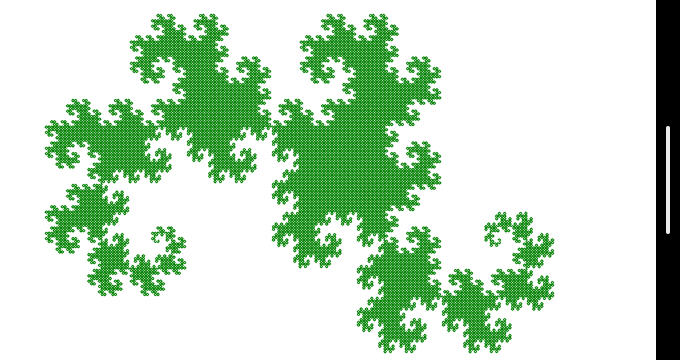
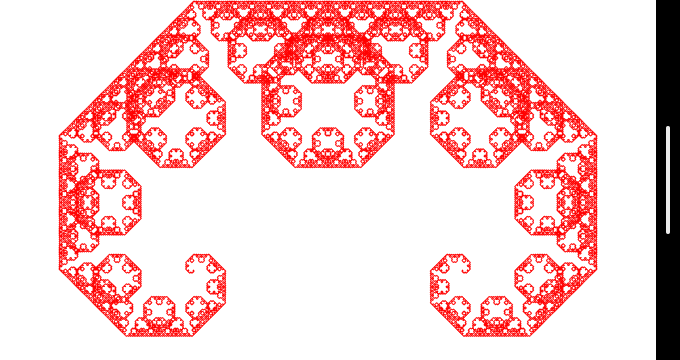
void demo()
{
double x1 = 100;
double x2 = 300;
double y = 150;
// the line segment
canvas.drawLine( x1, y, x2, y, "red" );
// a few points
double[] p1 = computePoint( x1, y, x2, y, 0.5, 0 ); // (blue) half along, does not move away
double[] p2 = computePoint( x1, y, x2, y, 0.5, 0.5 ); // (green) half along, moves half away
double[] p3 = computePoint( x1, y, x2, y, 0.75, 0.25 ); // (purple) 3/4 along, moves 1/4 away
canvas.drawSquare( x1, y, 8, "white(black)" ); // (black) starting point as square
canvas.drawCircle( p1[0], p1[1], 4, "white(blue)" );
canvas.drawCircle( p2[0], p2[1], 4, "white(green)" );
canvas.drawCircle( p3[0], p3[1], 4, "white(purple)" );
x1 = 300;
x2 = 100;
double y1 = 300;
double y2 = 500;
// the line segment
canvas.drawLine( x1, y1, x2, y2, "red" );
p1 = computePoint( x1, y1, x2, y2, 0.5, 0 ); // (blue) half along, does not move away
p2 = computePoint( x1, y1, x2, y2, 0.5, 0.5 ); // (green) half along, moves half away
p3 = computePoint( x1, y1, x2, y2, 0.75, 0.25 ); // (purple) 3/4 along, moves 1/4 away
canvas.drawSquare( x1, y1, 8, "white(black)" ); // (black) starting point as square
canvas.drawCircle( p1[0], p1[1], 4, "white(blue)" );
canvas.drawCircle( p2[0], p2[1], 4, "white(green)" );
canvas.drawCircle( p3[0], p3[1], 4, "white(purple)" );
}